Heart care delivered by a world-renowned UK cardiologist.
Trusted by patients worldwide, we deliver personalised cardiac care with unmatched expertise. Combining cutting-edge innovation and compassionate support, your heart health is always in the best hands.
Symptoms
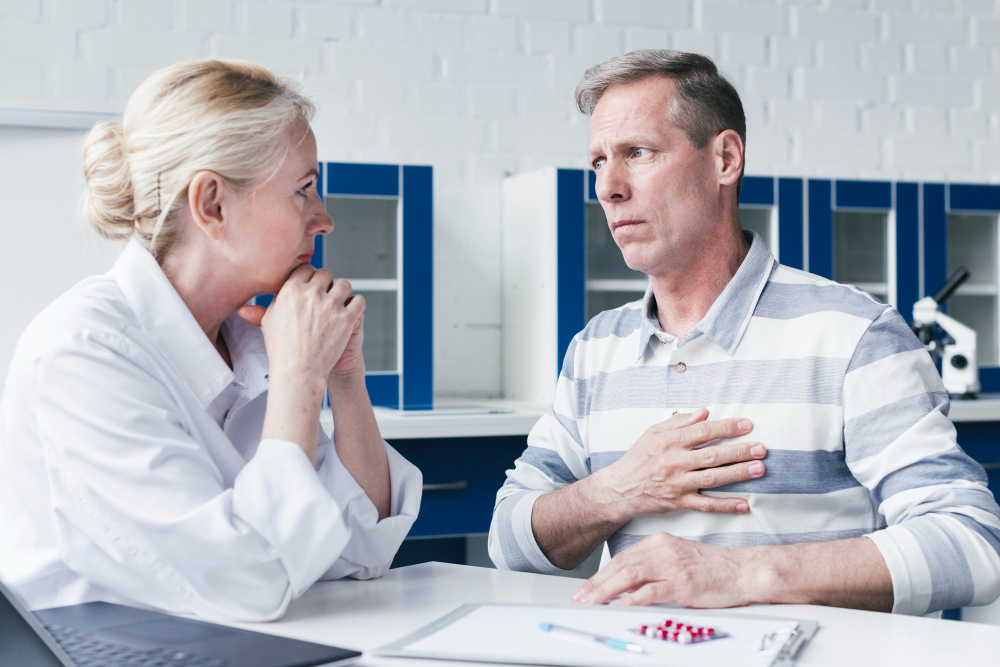
Understand the warning signs your heart may be giving you. Explore common symptoms like chest pain, breathlessness, and palpitations — and learn when to seek expert care.

Conditions
Learn more about common and complex heart conditions, from arrhythmias to coronary artery disease. With world-leading expertise, we guide you to the right diagnosis and advanced treatment options.

Treatments
Discover a comprehensive range of advanced cardiac treatments, from state-of-the-art diagnostics to minimally invasive procedures. Each approach is personalised to protect, treat, and strengthen your heart.
About Dr Suneil Aggarwal
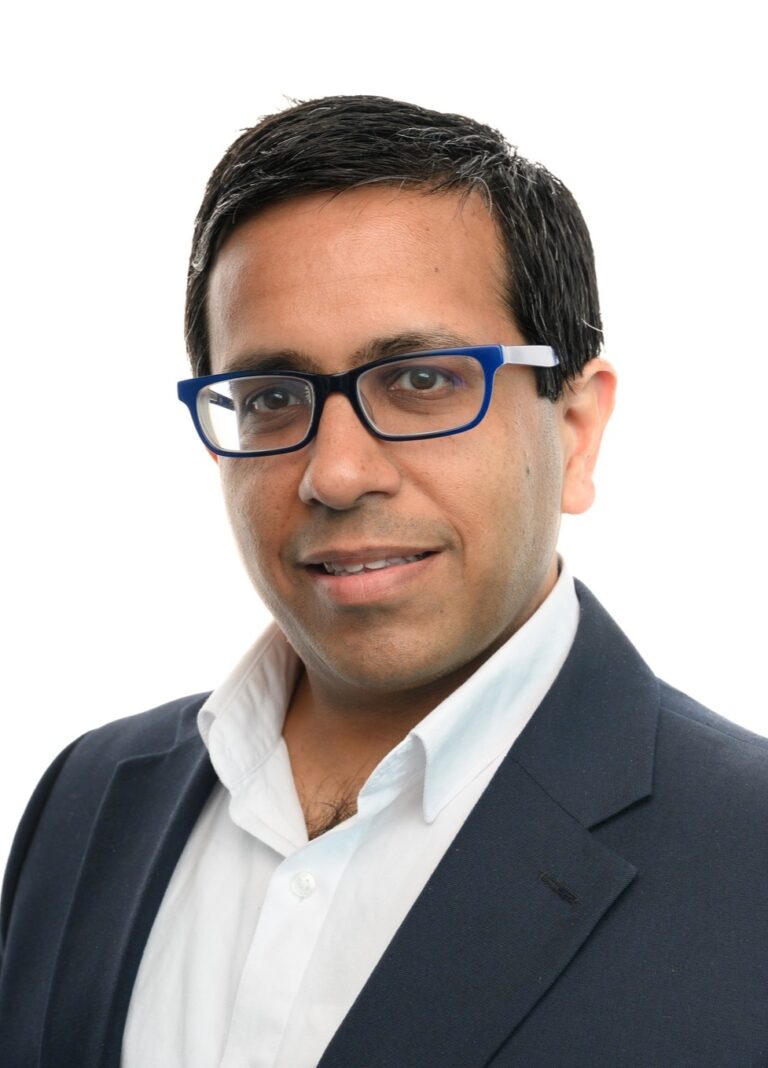

Dr Suneil Aggarwal is an Interventional Cardiologist specialising in valve and congenital heart disease interventions (structural intervention), as well as general cardiology. He qualified with multiple distinctions and prizes from University College London in 2002 and completed his postgraduate training in Oxford, India (Puttaparthi) and London.
He completed an MD research degree from University College London and a 2 year fellowship in TAVI and congenital interventions at The Heart Hospital and Barts Heart Centre in 2015. He has been practicing as Lead for Structural Intervention in Liverpool for the last 9 years, where he developed the service into one of the largest in the UK. He has now relocated to Barts Heart Centre to practice at what is one of the largest cardiac centres in Europe. He has particular expertise in TAVI, mitral interventions, PFO/ASD closure and other complex congenital and valve interventions. He is actively involved in research and training of the next generation of interventional cardiologists, and is regularly invited to speak around the world. As well as this, he regularly participates in voluntary work abroad. His reputation amongst his peers is reflected in being thrice elected to the Council of the British Cardiovascular Intervention Society, the national society for interventional cardiologists. He is now the National Lead for Structural Intervention, which includes PFO closure, TAVI and other valve interventions and congenital heart disease interventions.
Symptoms

Chest Pain
Chest pain is a common symptom with many possible causes, ranging from harmless to serious, and should always be assessed carefully for any underlying heart condition.

Palpitations
Palpitations are the sensation of an abnormal or noticeable heartbeat, often harmless but sometimes a sign of an underlying heart rhythm condition that should be assessed.

Shortness of Breath
Shortness of breath is the sensation of difficulty breathing, which may occur during activity or at rest and may range from mild discomfort to severe difficulty breathing.
Our Client Reviews
Conditions

Aortic Stenosis
A condition where the aortic valve — one of the heart’s key valves — becomes narrowed, stiff, or unable to open fully.
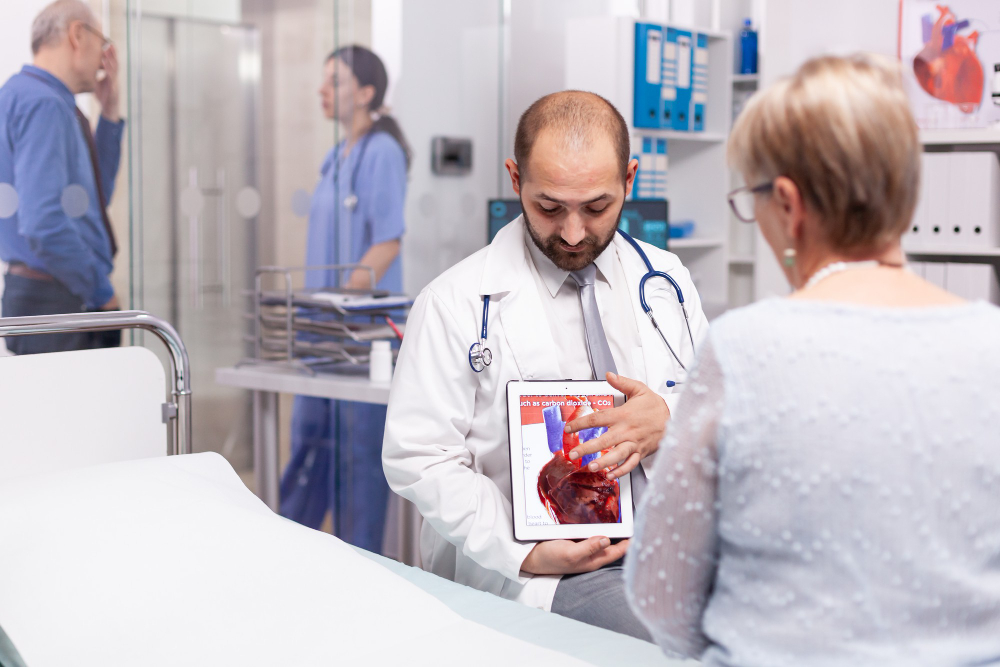
Aortic Regurgitation
A condition in which the aortic valve does not close completely, allowing some blood to leak back into the heart after each beat.

Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)
An ASD is a hole between the heart’s upper chambers that allows excess blood to flow to the right side, placing strain on the heart.
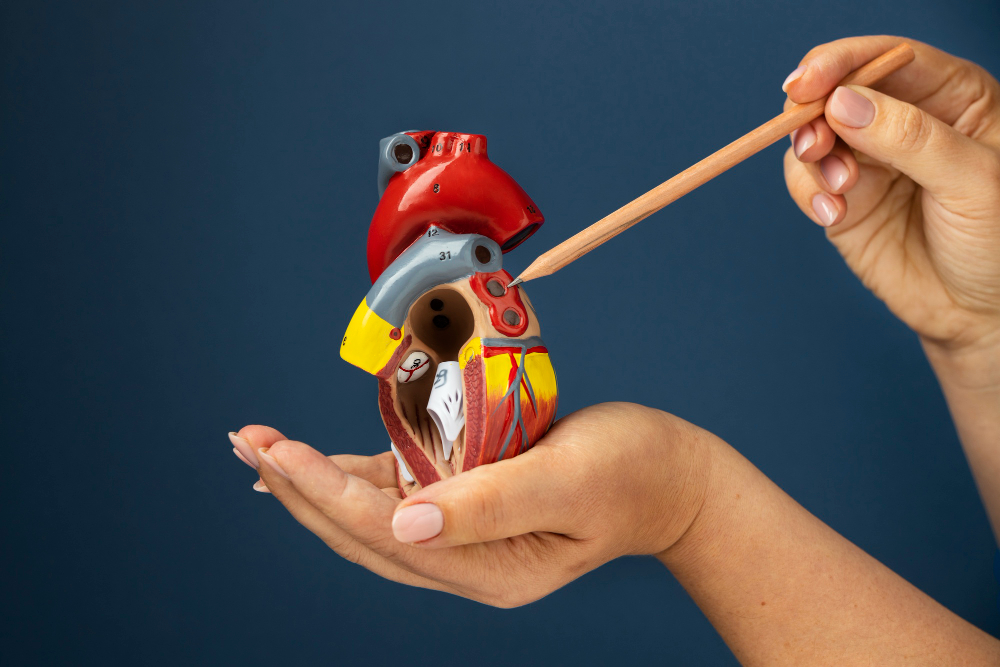

Coarctation of the Aorta
It is a narrowing of the body’s main artery that restricts blood flow and forces the heart to work harder, leading to high blood pressure.
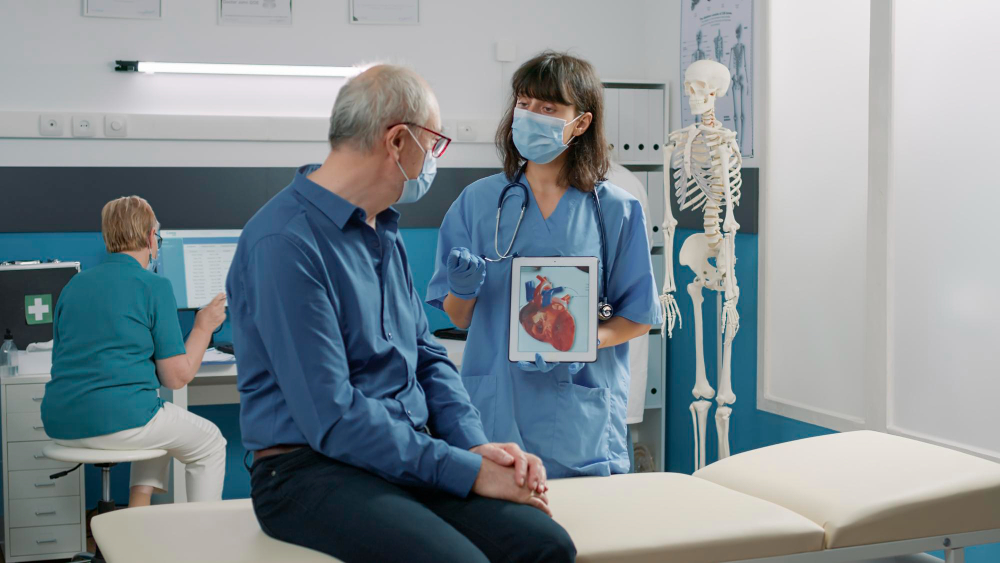
Mitral Regurgitation
It occurs when the mitral valve does not close fully, causing blood to leak backwards and making the heart work harder over time.

Patent Foramen Ovale (PFO)
It is a small flap between the heart’s upper chambers that fails to close after birth in some people, usually harmless but occasionally allowing blood to pass between the Atria.
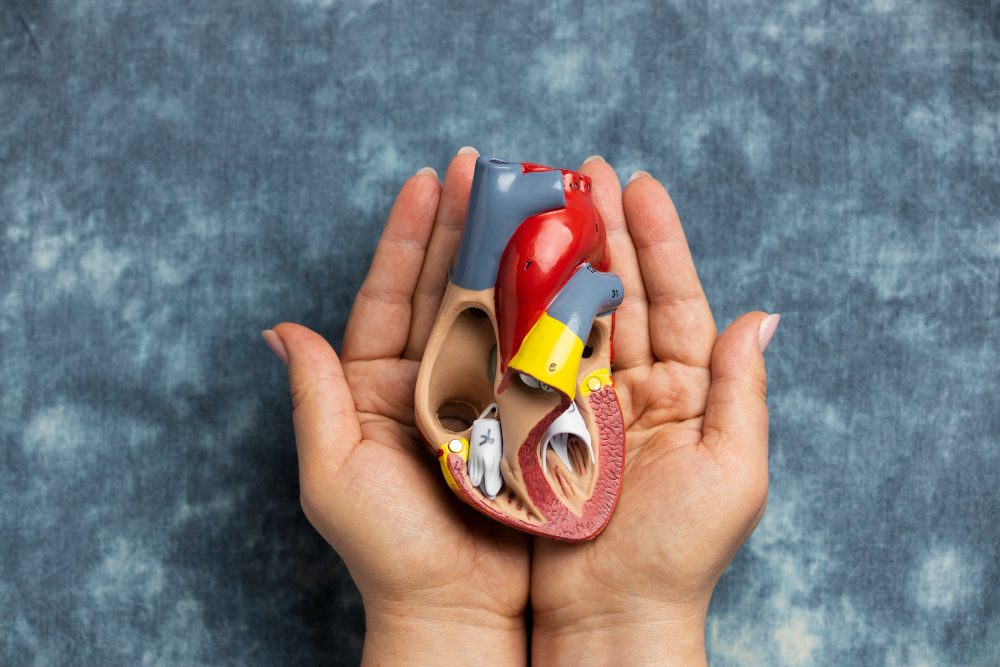
Mitral Stenosis
It is a narrowing of the mitral valve that restricts blood flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle, increasing pressure in the heart and lungs over time.
Pulmonary Valve Disease
It involves narrowing or leakage of the valve controlling blood flow from the right ventricle to the lungs, placing strain on the heart and affecting circulation over time.

Tricuspid Regurgitation
It occurs when the tricuspid valve fails to close properly, allowing blood to leak backwards and placing increasing strain on the right side of the heart over time.
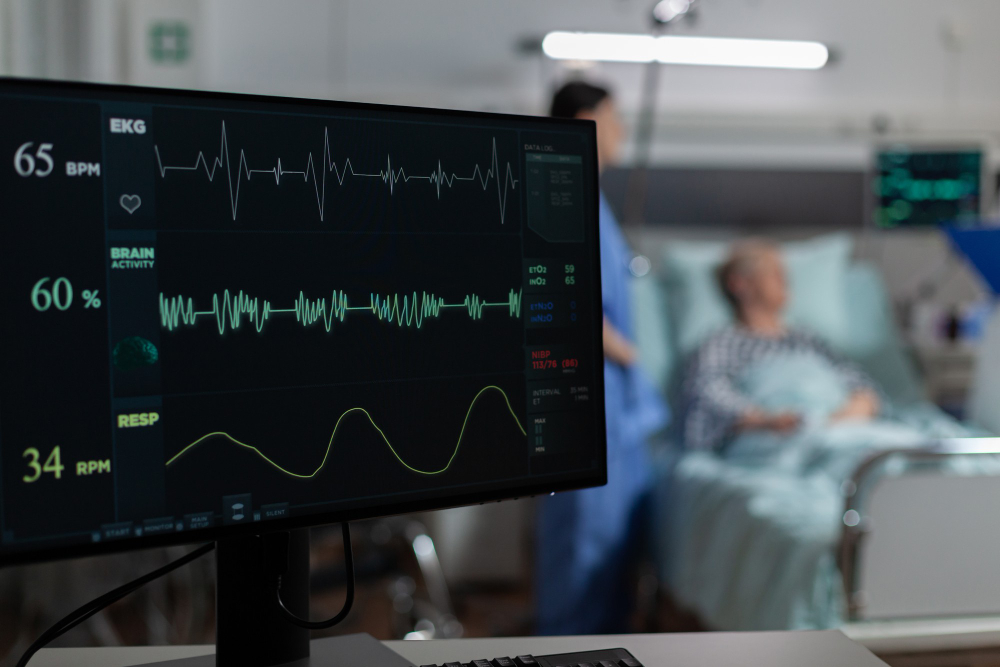
Diagnostic Tests
State-of-the-art diagnostic testing to accurately assess your heart health and guide treatment decisions.
Bubble Echocardiogram
A bubble echocardiogram — sometimes called a “bubble study” — is a specialised type of ultrasound scan that uses tiny, harmless bubbles to help detect small openings between the chambers of the heart.
Cardiac CT
A cardiac CT scan uses advanced X-ray technology to produce detailed, high-resolution images of your heart and its blood vessels.
Cardiac MRI
A cardiac MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is an advanced, non-invasive scan that uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to create highly detailed images of your heart.
Coronary Angiography
A coronary angiography (also known as a coronary angiogram or cardiac catheterisation) is a specialist test that allows your cardiologist to examine the blood vessels supplying your heart, known as the coronary arteries.
ECG
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a quick, simple, and completely painless test that records the electrical activity of your heart.
Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram (often referred to as an “echo”) is a safe and painless ultrasound scan that uses sound waves to create moving, detailed images of your heart.
Exercise Test
An exercise test — also known as an exercise ECG or treadmill test — measures how your heart responds to physical activity.
Heart Rhythm
A heart rhythm monitor is a small, wearable device that continuously records your heart’s electrical activity for 24–48 hours, or sometimes longer.
Stress Echocardiogram
A stress echocardiogram assesses how your heart and valves perform when your heart is working harder — either through physical exercise or with medication that safely mimics the effects of exercise.
Transoesophageal Echocardiogram
A transoesophageal echocardiogram (TOE) is a specialised ultrasound scan that captures detailed images of your heart from inside the oesophagus (food pipe).
24-Hour BP Monitor
A 24-hour blood pressure monitor measures your blood pressure automatically at regular intervals throughout the day and night.
Treatments
Evidence-based cardiac treatments focused on long-term heart health.
1
Mitral Transcatheter Edge-to-Edge Repair
A minimally invasive treatment for leaky heart valves, such as the mitral or tricuspid valve, that improves valve function without surgery. TEER can ease symptoms like breathlessness and fatigue while preserving the heart’s natural structure.
2
PDO/ASD Closure
A minimally invasive procedure to seal an opening between the heart’s upper chambers, helping to reduce stroke risk and normalise blood flow. Most patients recover quickly with little disruption to daily life.
3
TAVI
An advanced, catheter-based treatment for severe aortic stenosis that replaces the narrowed valve without open-heart surgery. It relieves symptoms, improves quality of life, and allows for a faster recovery.
Our Blogs
Clinic Locations
Multiple locations, one standard of exceptional heart care.







